Difference between revisions of "Sarsasapogenin"
Physchim62 (talk | contribs) |
Physchim62 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''Sarsasapogenin''' is a [[steroid]]. | + | '''Sarsasapogenin''' is a [[steroid]]al [[sapogenin]], that is the aglycosidic portion of a plant [[saponin]]. It is named after [[sarsaparilla]] (''[[Smilax]]'' sp.), a family of climbing plants found in subtropical regions. It was one of the first sapogenins to be identified, and the first [[spirostan]] steroid to be identified as such. The identification of the spirostan structure, with its ketone spiro acetal functionality, was fundamental in the development of the [[Marker degradation]], which allowed the industrial production of [[progesterone]] and other [[sex hormone]]s from plant steroids. |
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 12:38, 7 March 2010
| Sarsasapogenin | |
|---|---|
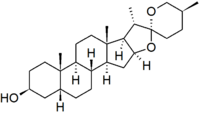
| |
| IUPAC name | (3β,5β,25S)-spirostan-3-ol |
| Identifiers | |
| InChI | InChI=1/C27H44O3/c1-16-7-12-27 (29-15-16)17(2)24-23(30-27)14- 22-20-6-5-18-13-19(28)8-10-25( 18,3)21(20)9-11-26(22,24)4/h16 -24,28H,5-15H2,1-4H3/t16-,17-, 18+,19-,20+,21-,22-,23-,24-,25 -,26-,27+/m0/s1 |
| InChIKey | GMBQZIIUCVWOCD-WWASVFFGBR |
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C27H44O3/c1-16-7-12-2 7(29-15-16)17(2)24-23(30-27)14 -22-20-6-5-18-13-19(28)8-10-25 (18,3)21(20)9-11-26(22,24)4/h1 6-24,28H,5-15H2,1-4H3/t16-,17- ,18+,19-,20+,21-,22-,23-,24-,2 5-,26-,27+/m0/s1 |
| Standard InChIKey | GMBQZIIUCVWOCD-WWASVFFGSA-N |
| CAS number | [] |
| EC number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Properties[1] | |
| Chemical formula | C27H44O3 |
| Molar mass | 416.64 g/mol |
| Melting point |
199–199.5 °C |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
Sarsasapogenin is a steroidal sapogenin, that is the aglycosidic portion of a plant saponin. It is named after sarsaparilla (Smilax sp.), a family of climbing plants found in subtropical regions. It was one of the first sapogenins to be identified, and the first spirostan steroid to be identified as such. The identification of the spirostan structure, with its ketone spiro acetal functionality, was fundamental in the development of the Marker degradation, which allowed the industrial production of progesterone and other sex hormones from plant steroids.
References
- ↑ Jacobs, Walter A.; Simpson, James C. E. On Sarsasapogenin and Gitogenin. J. Biol. Chem. 1934, 105 (3), 501–10, <http://www.jbc.org/content/105/3/501.full.pdf>.
External links
| Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination |
This page is currently licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license and any later versions of that license. |