Difference between revisions of "Nomenclature of steroids"
Physchim62 (talk | contribs) (→Parent hydride names) |
Physchim62 (talk | contribs) (→Numbering) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | The '''nomenclature of steroids''' is a subset of the [[nomenclature of natural products]].<ref name="NatProds">{{IUPAC natural products 1999}}.</ref> | + | The '''nomenclature of steroids''' is a subset of the [[nomenclature of natural products]].<ref name="NatProds" name="IUPAC99">{{IUPAC natural products 1999}}.</ref><ref name="IUPAC89">{{IUPAC-IUB steroids 1989}}.</ref> |
==Definitions== | ==Definitions== | ||
| − | A [[steroid]] is a compound (either naturally occurring or artificial) based on the cyclopenta[''a'']phenanthrene carbon skeleton, partially or completely hydrogenated.<ref name="GoldBook">{{GoldBookRef|title=steroids|file=S06005|accessdate=2010-03-08}}.</ref><ref name="ClassNames">{{IUPAC class names 1995|page=1367}}.</ref> Steroids usually have methyl groups at C-10 and C-13, and often an alkyl group at C-17 (termed a "side chain"). By extension, one or more bond scissions, ring expansions and/or ring contractions of the skeleton may have occurred.<ref name="GoldBook"/><ref name="ClassNames"/> [[Sterol]]s are steroids with a hydroxyl group at C-3.<ref name="ClassNames"/> | + | [[File:Steroid nucleus.png|thumb|right|The cyclopenta[''a'']phenanthrene carbon skeleton, with the conventional labelling of the four rings A–D.]] |
| + | A [[steroid]] is a compound (either naturally occurring or artificial) based on the cyclopenta[''a'']phenanthrene carbon skeleton, partially or completely hydrogenated.<ref name="GoldBook">{{GoldBookRef|title=steroids|file=S06005|accessdate=2010-03-08}}.</ref><ref name="ClassNames">{{IUPAC class names 1995|page=1367}}.</ref> Steroids usually have methyl groups at C-10 and C-13, and often an alkyl group at C-17 (termed a "side chain"). By extension, one or more bond scissions, ring expansions and/or ring contractions of the skeleton may have occurred.<ref name="GoldBook"/><ref name="ClassNames"/> [[Sterol]]s are steroids with a hydroxyl group at C-3.<ref name="ClassNames"/><ref group="note">The IUPAC–IUB Recommendations 1989 give a more restrictive definition of "sterol", in which the compound must have "most" of the [[cholestane]] side chain present at carbon-17. This definition, which excludes the 3-hydroxy sex hormones, appears to have been superseded in chemical nomenclature.</ref> | ||
| − | == | + | For historical reasons, there are two groups of compounds based on the cyclopenta[''a'']phenanthrene carbon skeleton that are nor normally classed as steroids, at least for nomenclature purposes:<ref name="IUPAC89"/> |
| + | *The [[Terpene|triterpenes]] [[dammarane]], [[lanostane]] and [[protostane]], which are biosynthetically related to the steroids but usually named using [[Nomenclature of terpenes and terpenoids|terpene nomenclature]]; (to which list could be added the diterpene [[labdane]] and the triterpenes [[gammacerane]], [[lupane]], [[oleanane]] and [[ursane]], all structurally related to the steroids) | ||
| + | *The steroid [[alkaloids]], nitrogen-containing compounds that have much greater structural diversity: possible examples that could conceivably be named using steroid nomenclature include [[cevane]], [[conanine]], [[chelidonine]], [[emetan]], [[samandarine]], [[spirosolane]] and [[solanidine]], the last two showing the most obvious structural relationships with other steroids. | ||
| + | The various forms of [[Vitamin D]] can be named as steroids (9,10-secoergostane derivatives), a practice which mirrors their biosynthetic pathway. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Principles== | ||
| + | {{main|Nomenclature of natural products}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Specificities== | ||
| + | ===Numbering=== | ||
| + | [[File:Steroid nucleus numbering.png|thumb|right|209px|The conventional numbering of the carbon atoms of the steroid nucleus and the two methyl groups which are often present at carbons-10 and -13. The numbering of the side chain at carbon-17 (if present) starts from C-20.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===α/β notation=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Fundamental parent structures== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! | + | ! Name |
! Structure | ! Structure | ||
! width=200px | Notes | ! width=200px | Notes | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[gonane]] | | [[gonane]] | ||
| − | | | + | | [[File:Gonane.png|179px]] |
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[estrane]] | | [[estrane]] | ||
| − | | | + | | [[File:Estrane.png|179px]] |
| "estrane" is the IUPAC preferred spelling; older British texts may spell it as "oestrane" | | "estrane" is the IUPAC preferred spelling; older British texts may spell it as "oestrane" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[androstane]] | | [[androstane]] | ||
| − | | | + | | [[File:Androstane.png|179px]] |
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[pregnane]] | | [[pregnane]] | ||
| − | | | + | | [[File:Pregnane.png|207px]] |
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[cholane]] | | [[cholane]] | ||
| − | | | + | | [[File:Cholane.png|240px]] |
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[cholestane]] | | [[cholestane]] | ||
| − | | | + | | [[File:Cholestane.png|292px]] |
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[ergostane]] | | [[ergostane]] | ||
| − | | | + | | [[File:Ergostane.png|292px]] |
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[campestane]] | | [[campestane]] | ||
| − | | | + | | [[File:Campestane.png|292px]] |
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[poriferastane]] | | [[poriferastane]] | ||
| − | | | + | | [[File:Poriferastane.png|292px]] |
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[stigmastane]] | | [[stigmastane]] | ||
| − | | | + | | [[File:Stigmastane.png|292px]] |
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[gorgostane]] | | [[gorgostane]] | ||
| [[File:Gorgostane.png|292px]] | | [[File:Gorgostane.png|292px]] | ||
| − | | | + | | numbering of the side chain is non-systematic in CAS nomenclature |
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| [[cardanolide]] | | [[cardanolide]] | ||
| [[File:Cardanolide.png|234px]] | | [[File:Cardanolide.png|234px]] | ||
| − | | | + | | |
|- | |- | ||
| [[bufanolide]] | | [[bufanolide]] | ||
| − | | | + | | [[File:Bufanolide.png|189px]] |
| | | | ||
|- | |- | ||
| [[furostan]] | | [[furostan]] | ||
| − | | | + | | [[File:Furostan.png|312px]] |
| − | | | + | | configuration at C-22 must be specified for each derivative |
|- | |- | ||
| [[spirostan]] | | [[spirostan]] | ||
| [[File:Spirostan.png|286px]] | | [[File:Spirostan.png|286px]] | ||
| − | | configuration at | + | | configuration at C-25 must be specified for each derivative |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | ==References== | + | ==Notes and references== |
| − | {{reflist}} | + | ===Notes=== |
| + | {{reflist|group=note}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | {{reflist|2}} | ||
[[Category:Nomenclature of steroids|*]] | [[Category:Nomenclature of steroids|*]] | ||
Latest revision as of 06:32, 10 March 2010
The nomenclature of steroids is a subset of the nomenclature of natural products.[1][2]
Contents
Definitions
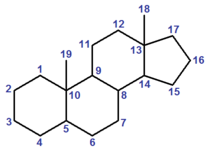
A steroid is a compound (either naturally occurring or artificial) based on the cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene carbon skeleton, partially or completely hydrogenated.[3][4] Steroids usually have methyl groups at C-10 and C-13, and often an alkyl group at C-17 (termed a "side chain"). By extension, one or more bond scissions, ring expansions and/or ring contractions of the skeleton may have occurred.[3][4] Sterols are steroids with a hydroxyl group at C-3.[4][note 1]
For historical reasons, there are two groups of compounds based on the cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene carbon skeleton that are nor normally classed as steroids, at least for nomenclature purposes:[2]
- The triterpenes dammarane, lanostane and protostane, which are biosynthetically related to the steroids but usually named using terpene nomenclature; (to which list could be added the diterpene labdane and the triterpenes gammacerane, lupane, oleanane and ursane, all structurally related to the steroids)
- The steroid alkaloids, nitrogen-containing compounds that have much greater structural diversity: possible examples that could conceivably be named using steroid nomenclature include cevane, conanine, chelidonine, emetan, samandarine, spirosolane and solanidine, the last two showing the most obvious structural relationships with other steroids.
The various forms of Vitamin D can be named as steroids (9,10-secoergostane derivatives), a practice which mirrors their biosynthetic pathway.
Principles
Specificities
Numbering
α/β notation
Fundamental parent structures
| Name | Structure | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| gonane | 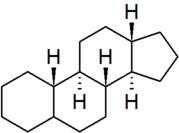
|
|
| estrane | 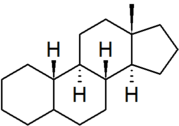
|
"estrane" is the IUPAC preferred spelling; older British texts may spell it as "oestrane" |
| androstane | 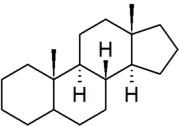
|
|
| pregnane | 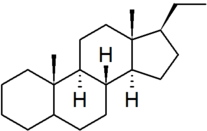
|
|
| cholane | 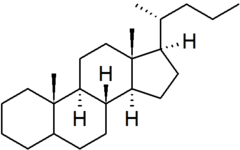
|
|
| cholestane | 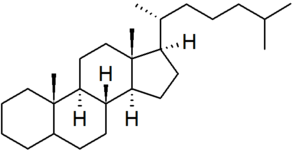
|
|
| ergostane | 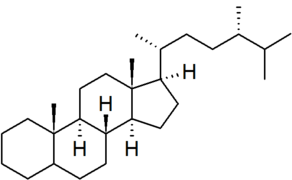
|
|
| campestane | 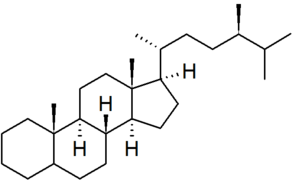
|
|
| poriferastane | 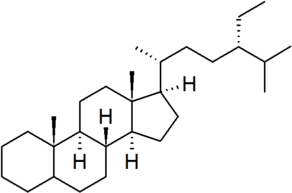
|
|
| stigmastane | 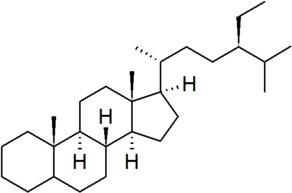
|
|
| gorgostane | 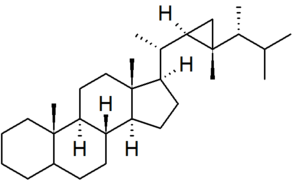
|
numbering of the side chain is non-systematic in CAS nomenclature |
| cardanolide | 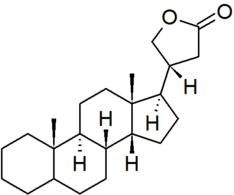
|
|
| bufanolide | 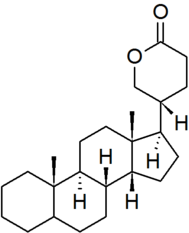
|
|
| furostan | 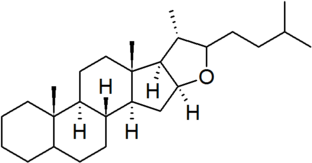
|
configuration at C-22 must be specified for each derivative |
| spirostan | 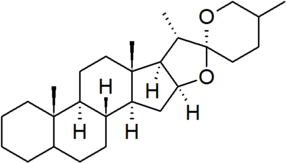
|
configuration at C-25 must be specified for each derivative |
Notes and references
Notes
- ↑ The IUPAC–IUB Recommendations 1989 give a more restrictive definition of "sterol", in which the compound must have "most" of the cholestane side chain present at carbon-17. This definition, which excludes the 3-hydroxy sex hormones, appears to have been superseded in chemical nomenclature.
References
- ↑ Revised Section F: Natural Products and Related Compounds (IUPAC Recommendations 1999). Pure Appl. Chem., 71 (4), 587–643. DOI: 10.1351/pac199971040587.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Nomenclature of Steroids (IUPAC–IUB Recommendations 1989). Pure Appl. Chem., 61 (10), 1783–1822. DOI: 10.1351/pac198961101783.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 steroids, <http://goldbook.iupac.org/S06005.html> (accessed 8 March 2010), Compendium of Chemical Terminology Internet edition; International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Glossary of class names of organic compounds and reactivity intermediates based on structure (IUPAC Recommendations 1995). Pure Appl. Chem. 1995, 67 (8-9), 1307–75 at 1367. DOI: 10.1351/pac199567081307.
| Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination |
This page is currently licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license and any later versions of that license. |