Difference between revisions of "Education:ExampleProductB"
(Create page) |
m (tweak) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File:ExampleProductB.png|200px|center]] | [[File:ExampleProductB.png|200px|center]] | ||
| − | <big>INCORRECT!</big> | + | <span style="color:red"><big>'''INCORRECT!'''</big></span> |
;Type of reaction | ;Type of reaction | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
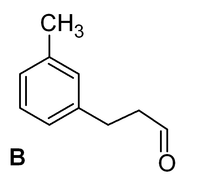
;Position of C=O | ;Position of C=O | ||
[[File:Red x small.PNG|15px|left]] | [[File:Red x small.PNG|15px|left]] | ||
| − | The product of acylation should have the carbonyl C=O next to the ring. This is because this group becomes the electrophile that attacks the ring. The product | + | The product of acylation should have the carbonyl C=O next to the ring. This is because this group becomes the electrophile that attacks the ring. The product B shown would need the methyl end of the chain to react as electrophile - very unlikely! |
[[Category:ChemSpider Education]] | [[Category:ChemSpider Education]] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:18, 2 September 2010
INCORRECT!
- Type of reaction
This is a Friedel-Crafts acylation, which is a type of electrophilic aromatic substitution that occurs on aromatic rings that are not strongly deactivated.
- Position of attack
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
The methyl group directs the attack ortho/para, so this product (from meta attack) is substituted at the wrong position.
- Position of C=O
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
The product of acylation should have the carbonyl C=O next to the ring. This is because this group becomes the electrophile that attacks the ring. The product B shown would need the methyl end of the chain to react as electrophile - very unlikely!