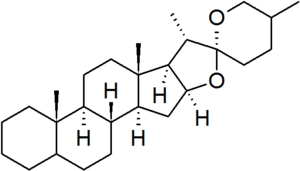Difference between revisions of "Spirostan"
Physchim62 (talk | contribs) |
Physchim62 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[File:Spirostan.png|thumb|right]] | + | [[File:Spirostan.png|thumb|right|The spirostan fundamental parent structure.]] |
| − | '''Spirostan''' is a defined [[fundamental parent structure]] in the [[nomenclature of steroids]].<ref>{{IUPAC natural products 1999}}.</ref><ref>{{IUPAC-IUB steroids 1989}}.</ref> It is characterised by a bicyclic side chain containing a [[ketone]] [[spiro]] [[acetal]] group. In the spirostan structure, the configurations of carbons 5 and 25 are not defined, and so must be specified for each derivative. Spirostan steroids are common as the [[Glycoside|aglycosidic]] portions of plant [[saponin]]s, and include: | + | [[File:Spirostan side-chain alt.png|An alternative depiction of the spirostan side chain, emphasizing the fact that rings E and F are perpendicular to one another. Carbon-25 is shown with an (''R'')-configuration in this diagram.]] |
| + | '''Spirostan''' is a defined [[fundamental parent structure]] in the [[nomenclature of steroids]].<ref>{{IUPAC natural products 1999}}.</ref><ref>{{IUPAC-IUB steroids 1989}}.</ref> It is characterised by a bicyclic side chain containing a [[ketone]] [[spiro]] [[acetal]] group. In the spirostan structure, the configurations of carbons 5 and 25 are not defined, and so must be specified for each derivative. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Occurrence== | ||
| + | Spirostan steroids are common as the [[Glycoside|aglycosidic]] portions of plant [[saponin]]s, and include: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
Revision as of 07:14, 11 March 2010
Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
Spirostan is a defined fundamental parent structure in the nomenclature of steroids.[1][2] It is characterised by a bicyclic side chain containing a ketone spiro acetal group. In the spirostan structure, the configurations of carbons 5 and 25 are not defined, and so must be specified for each derivative.
Occurrence
Spirostan steroids are common as the aglycosidic portions of plant saponins, and include:
| C-5 | C-25 | Other | |
|---|---|---|---|
| sarsasapogenin | β | S | 3β-OH |
| smilagenin | β | R | 3β-OH |
| tigogenin | α | R | 3β-OH |
| diosgenin | Δ5 | R | 3β-OH |
| anzurogenin-D | α | R | 3β-OH, 5α-OH, 6β-OH |
| sisalgenin | α | S | 3β-OH, C=O at C-12 |
| roscogenin | Δ5 | S | 1β-OH, 3β-OH |
References
- ↑ Revised Section F: Natural Products and Related Compounds (IUPAC Recommendations 1999). Pure Appl. Chem., 71 (4), 587–643. DOI: 10.1351/pac199971040587.
- ↑ Nomenclature of Steroids (IUPAC–IUB Recommendations 1989). Pure Appl. Chem., 61 (10), 1783–1822. DOI: 10.1351/pac198961101783.
| Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination |
This page is currently licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license and any later versions of that license. |