Propan-1-ol
| Propanol | |
|---|---|

| |

| |

| |
| IUPAC name | propan-1-ol |
| Other names | 1-propanol propyl alcohol n-propanol n-propyl alcohol propanol |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | [] |
| RTECS | UH8225000 |
| ChemSpider | |
| SMILES | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C3H8O |
| Molar mass | 60.10 g/mol |
| Appearance | Clear, colourless liquid |
| Density | 0.8034 g/cm3, liquid |
| Melting point |
−126.5 °C (146.7 K) |
| Boiling point |
97.1 °C (370.3 K) |
| Solubility in water | Fully miscible |
| Acidity (pKa) | (~16) |
| Viscosity | 1.938 cP at 25°C |
| Structure | |
| Dipole moment | 1.68 D |
| Hazards | |
| EU classification | Flammable (F) Irritant (Xi) |
| R-phrases | Template:R11, Template:R41, Template:R67 |
| S-phrases | Template:S2, Template:S7, Template:S16, Template:S24, Template:S26, Template:S39 |
| NFPA 704 | |
| Flash point | 15 °C |
| Related compounds | |
| Other alcohols | Ethanol Propan-2-ol Butan-1-ol |
| Other compounds | Propionaldehyde Propionic acid 1-Chloropropane Propyl acetate |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
Propan-1-ol is a primary alcohol with the Molecular formula of C3H8O. It is also known as 1-propanol, 1-propyl alcohol, n-propyl alcohol, or simply propanol. It is an isomer of propan-2-ol. It is used as a solvent in the pharmaceutical industry, and for resins and cellulose esters. It is formed naturally in small amounts during many fermentation processes.
Chemical properties
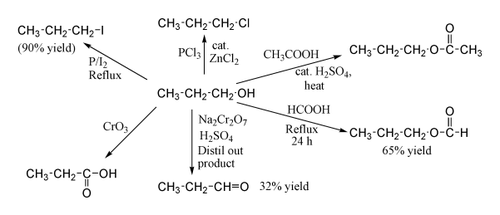
1-Propanol shows the normal reactions of a primary alcohol. Thus it can be converted to alkyl halides; for example red phosphorus and iodine produce n-propyl iodide in 90% yield, while PCl3 with catalytic ZnCl2 gives 1-chloropropane. Reaction with acetic acid in the presence of an H2SO4 catalyst under Fischer esterification conditions gives propyl acetate, while refluxing propanol overnight with formic acid alone can produce propyl formate in 65% yield. Oxidation of 1-propanol with Na2Cr2O7 and H2SO4 gives only a 36% yield of propionaldehyde, and therefore for this type of reaction higher yielding methods using PCC or the Swern oxidation are recommended. Oxidation with chromic acid yields propionic acid
Preparation
1-Propanol is a major constituent of fusel oil, a by-product formed from certain amino acids when potatoes or grains are fermented to produce ethanol. This is no longer a significant source of propanol.
1-Propanol is manufactured by catalytic hydrogenation of propionaldehyde. The propionaldehyde is itself produced via the oxo process, by hydroformylation of ethylene using carbon monoxide and hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst such as cobalt octacarbonyl or a rhodium complex.
- (1) H2C=CH2 + CO + H2 → CH3CH2CH=O
- (2) CH3CH2CH=O + H2 → CH3CH2CH2OH
A traditional laboratory preparation of 1-propanol involves treating n-propyl iodide with moist Ag2O.
History
1-Propanol was discovered in 1853 by Chancel, who obtained it by fractional distillation of fusel oil.
References
- Furniss, B. S.; Hannaford, A. J.; Smith, P. W. G.; Tatchell, A. R. Vogel's Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry, 5th ed.; Longman: Harlow, 1989. ISBN 0-582-46236-3
- (2006-06-26) CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 87th Edition, 87, TF-CRC. ISBN 0849304873.
- (2006-11-03) in Maryadele J. O'Neil: The Merck Index: An Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals, 14, Merck. ISBN 091191000X.
- (1922) Organic Chemistry. London: W. & R. Chambers.
External links
Template:Alcohols Template:Antiseptics and disinfectants
| Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination | |
This page was originally imported from Wikipedia, specifically this version of the article "Propan-1-ol". Please see the history page on Wikipedia for the original authors. This WikiChem article may have been modified since it was imported. It is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution–Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. |