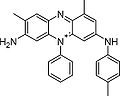
Mauveine
Mauveine, also known as aniline purple and Perkin's mauve, was the first synthetic organic dye.[1][2] Its chemical name is 3-amino-2,±9-dimethyl-5-phenyl-7-(p-tolylamino)phenazinium acetate. The formula is C26H23N4+X− (mauveine A) and C27H25N4+X− (mauveine B, see below). Template:TOCnestright
History
Mauveine was discovered serendipitously in 1856 by 18-year old William Henry Perkin, who was trying to synthesize the antimalarial drug quinine as a challenge from his professor, August Wilhelm von Hofmann. In one of his attempts, Perkin oxidized aniline using potassium dichromate. Under these conditions, the aniline reacted with toluidine impurities in it to produce a black solid, a fairly common result in "failed" organic syntheses. While trying to clean out his flask, Perkin discovered that some component of the black solid dissolved in alcohol to give a purple-colored solution, which proved to be an effective dye for silk and other textiles.
Perkin patented the new dye and the following year he opened a dyeworks at Greenford on the banks[3] of the Grand Union Canal in London to mass produce it. It was originally manufactured under the name of aniline purple or Tyrian purple, also the name of an ancient mollusc-derived natural dye.[4] The name mauve was given to it in England in early 1859, from the French name for the mallow flower, and chemists later called it mauveine.[4] Mauve became highly fashionable in 1862 when Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom appeared at the Royal Exhibition in a mauve silk gown. Mauve fell out of fashion in the late 1860s to newer synthetic colors, but not before making Perkin's fortune and birthing the synthetic chemical industry. The U.S. National Association of Confectioners included mauvein among permitted food colorings as of the early 20th century, with a variety of equivalent names: rosolan, violet paste, chrome violet, anilin violet, anilin purple, Perkins violet, indisin, phenamin, purpurin, tyralin, Tyrian purple, and lydin.[5] Later work on chemical dyes also led to the (accidental) development of modern chemotherapy (see Sulfonamide).
The color of this dye may be familiar due to its widespread use in spirit duplicator (trade name Ditto) printing machines, popular during the mid-20th century.
Chemical analysis
A modern-day laboratory procedure for the organic synthesis of mauveine consists of dissolving a mixture of aniline, p-toluidine and o-toluidine in sulfuric acid and water (large excess poor solubility) in roughly a 1:1:2 ratio followed by addition of potassium dichromate.[6] The actual molecular structure of mauveine proved difficult to determine and was not known with certainty until 1994.[7]
Skeletal formula of mauveine A Skeletal formula of mauveine B - Mauveine b2 skeletal org.jpg
Skeletal formula of mauveine B2 - Mauveine c skeletal org.jpg
Skeletal formula of mauveine C
It is actually a mixture of four related aromatic compounds, which differ only in the number and placement of methyl groups. Mauveine A is built up from 2 molecules of aniline, one of p-toluidine and one of o-toluidine whereas Mauveine B incorporates aniline, p-toluidine and o-toluidine one molecule each. As Perkin showed in 1879,[8] mauveine B is related to the safranines by oxidative/reductive loss of the p-tolyl group. In fact, safranine itself is a 2,8-dimethyl phenazinium salt, whereas the parasafranine produced by Perkin must be presumed[9] to be the 1,8-(or 2,9) dimethyl isomer.

In 2007, two other mauveine components were isolated and identified, called mauveine C (an additional p-methyl group on mauveine A) and mauveine B2 (an isomer of mauveine B with methyl on different aryl group). [10]
References
- ↑ Hubner, K. History – 150 Years of mauveine. Chemie in unserer Zeit 2006, 40 (4), 274–75. DOI: 10.1002/ciuz.200690054.
- ↑ Travis, Anthony S. Perkin’s Mauve: Ancestor of the Organic Chemical Industry. Technol. Cult. 1990, 31 (1), 51–82. DOI: 10.2307/3105760.
- ↑ Google Earth location: Download
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Matthew, H. C. G.; Harrison, Brian Howard Oxford Dictionary of National Biography; Oxford University Press: Oxford, 2004. ISBN 0198613938
- ↑ Leffmann, Henry; Beam, William Select Methods in Food Analysis; P. Blakiston's Son & Co.: Philadelphia, 1901, <http://books.google.com/books?id=oXI3AAAAMAAJ&pg=PA77&dq=perkins+tyrian.purple#PPA75,M1>
- ↑ Scaccia, Rhonda L.; Coughlin, David; Ball, David W. A Microscale Synthesis of Mauve. J. Chem. Educ. 1998, 75, 769. Abstract
- ↑ Meth-Cohn, O.; Smith, M. What did W. H. Perkin actually make when he oxidised aniline to obtain mauveine?. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin 1 1994, 5–7. DOI: 10.1039/P19940000005.
- ↑ Perkin, W. H. On mauveine and allied colouring matters. J. Chem. Soc., Trans. 1879, 717–32. DOI: 10.1039/CT8793500717.
- ↑ , <http://www.ch.ic.ac.uk/motm/perkin.html>.
- ↑ Seixas de Melo, J.; Takato, S.; Sousa, M.; Melo, M. J.; Parola, A. J. Revisiting Perkin's dye(s): the spectroscopy and photophysics of two new mauveine compounds (B2 and C). Chem. Commun. 2007, 2624–26. DOI: 10.1039/b618926a.
External links
| Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination | |
This page was originally imported from Wikipedia, specifically this version of the article "Mauveine". Please see the history page on Wikipedia for the original authors. This WikiChem article may have been modified since it was imported. It is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution–Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. |