Nomenclature of steroids
Revision as of 17:53, 8 March 2010 by Physchim62 (talk | contribs)
The nomenclature of steroids is a subset of the nomenclature of natural products.[1]
Definitions
A steroid is a compound (either naturally occurring or artificial) based on the cyclopenta[a]phenanthrene carbon skeleton, partially or completely hydrogenated.[2][3] Steroids usually have methyl groups at C-10 and C-13, and often an alkyl group at C-17 (termed a "side chain"). By extension, one or more bond scissions, ring expansions and/or ring contractions of the skeleton may have occurred.[2][3] Sterols are steroids with a hydroxyl group at C-3.[3]
Parent hydride names
| Parent hydride | Structure | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| androstane | ||
| bufanolide | ||
| campestane | ||
| cardanolide | 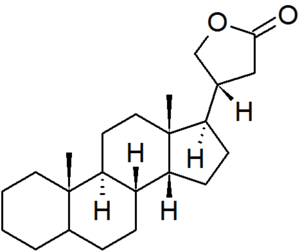
|
configuration at C-5 must be specified for each derivative |
| cholane | ||
| cholestane | ||
| ergostane | ||
| estrane | "estrane" is the IUPAC preferred spelling; older British texts may spell it as "oestrane" | |
| furostan | ||
| gonane | ||
| gorgostane | ||
| poriferastane | ||
| pregnane | ||
| spirostan | 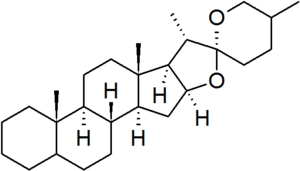
|
configuration at C-5 and C-25 must be specified for each derivative |
| stigmastane |
References
- ↑ Revised Section F: Natural Products and Related Compounds (IUPAC Recommendations 1999). Pure Appl. Chem., 71 (4), 587–643. DOI: 10.1351/pac199971040587.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 steroids, <http://goldbook.iupac.org/S06005.html> (accessed 8 March 2010), Compendium of Chemical Terminology Internet edition; International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Glossary of class names of organic compounds and reactivity intermediates based on structure (IUPAC Recommendations 1995). Pure Appl. Chem. 1995, 67 (8-9), 1307–75 at 1367. DOI: 10.1351/pac199567081307.
| Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination |
This page is currently licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license and any later versions of that license. |