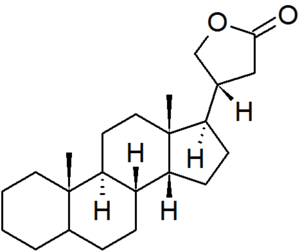
Cardanolide
Cardanolide is a defined fundamental parent structure in the nomenclature of steroids.[1][2] It is characterised by a γ-butyrolactone side chain, which is often further unsaturated giving cardenolides. In the cardanolide structure, the configuration of carbon-5 is not defined, and so must be specified for each derivative. Cardanolide steroids include the aglycosidic portions of the cardiac glycosides, such as digitoxigenin.
References
- ↑ Revised Section F: Natural Products and Related Compounds (IUPAC Recommendations 1999). Pure Appl. Chem., 71 (4), 587–643. DOI: 10.1351/pac199971040587.
- ↑ Nomenclature of Steroids (IUPAC–IUB Recommendations 1989). Pure Appl. Chem., 61 (10), 1783–1822. DOI: 10.1351/pac198961101783.
| Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination |
This page is currently licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license and any later versions of that license. |