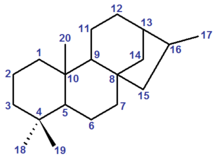
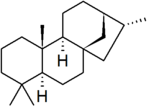Kaurane
Kaurane is a defined fundamental parent structure used in the IUPAC nomenclature of natural products and also, distinctly, in CAS nomenclature. It is a diterpene with a rigid four-ring structure and six chiral centres.
Contents
Ambiguity between IUPAC and CAS
The stereochemistry of the six chiral centres is defined by convention: however, IUPAC and CAS use different opposite enantiomers, which also leads to a slight difference in numbering between the two systems. IUPAC conventional kaurane has (5S,8S,9S,10S,13S,15R)-stereochemistry, and is drawn with the five-membered ring receding into the plane of the image.[1] CAS conventional kaurane has (5R,8R,9R,10R,13R,15S)-stereochemistry, and is drawn with the five-membered ring protruding from the plane of the image.[2] For the two methyl groups attached to carbon-4, the two number systems are identical (but see below): the methyl group receding into the plane of the image is numbered carbon-18 and the one protruding from the plane of the image is numbered carbon-19.[3][note 1]
ent-Kaurane
The name ent-kaurane is sometimes used to refer to the CAS conventional kaurane,[4] and so to distinguish it from the IUPAC stereochemistry, in particular by the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IUBMB).[5] This is the structure of the cyclic skeleton of all naturally occurring kaurane terpenes. However, the numbering system is distinct between CAS nomenclature and IUBMB nomenclature: the metabolic intermediate kaurenoic acid, which has the (4S)-configuration, is kaur-16-en-18-oic acid in CAS nomenclature but ent-kaur-16-en-19-oic acid in IUBMB nomenclature.[2][5][note 2]
Occurence
Kaurane diterpenes have been extracted from a variety of plant species,[4][6] in particular Stevia sp., the source of the steviol glycosides stevioside and rebaudioside-A that have been used as artificial sweetners.[7] They are intermediates in gibberellin biosynthesis, leading to a group of important plant hormones (gibberellins):[8] gibberellin A12 is biosynthesized from ent-kaurene by six successive oxidations catalyzed by ent-kaurene oxidase (EC 1.14.13.78) and ent-kaurenoic acid oxidase (EC 1.14.13.79).[5] The ent-kaurane skeleton is also found in veatchine and other Garrya alkaloids.[9]
Notes and references
Notes
- ↑ Note that the numbering on the structural diagrams in the appendix to the original version of the IUPAC Recommendations 1999 is incorrect.
- ↑ The reason for this difference is that the ent nomenclature operation reverses the configuration of every chiral centre in the molecule, and so maps C-19 onto C-18 and vice versa. This is clarified in the 2004 errata to the IUPAC Recommendations 1999.
References
- ↑ Revised Section F: Natural Products and Related Compounds (IUPAC Recommendations 1999). Pure Appl. Chem., 71 (4), 587–643. DOI: 10.1351/pac199971040587.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 57817-89-7 – Kaur-16-en-18-oic acid, 13-[(2-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-β-D-glucopyranosyl)oxy]-, β-D-glucopyranosyl ester, (4α)-. In Common Chemistry; Chemical Abstracts Service, <http://www.commonchemistry.org/ChemicalDetail.aspx?ref=57817-89-7>. (accessed 5 September 2009).
- ↑ Revised Section F: Natural products and related compounds (IUPAC Recommendations 1999). Corrections and modifications (2004). Pure Appl. Chem., 76 (6), 1283–92. DOI: 10.1351/pac200476061283.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Nagashima, Fumihiro; Tanaka, Hironao; Takaoka, Shigeru; Asakawa, Yoshinori Ent-kaurane-type diterpenoids from the liverwort Jungermannia exsertifolia ssp. cordifolia. Phytochemistry 1996, 41 (4), 1129–41. DOI: 10.1016/0031-9422(95)00755-5. Arriaga-Giner, Francisco Javier; Rumbero, Angel; Wollenweber, Eckhard 16α,19-Diacetoxy-ent-kaurane, a New Natural Diterpene from the Exudate of Ozothamnus scutellifolius (Asteraceae). Z. Naturforsch. C 1999, 54, 602–4. Harinantenaina, Liva Rakotondraibe Romuald; Kasai, Ryoji; Yamasaki, Kazuo Ent-kaurane Diterpenoid Glycosides from the Leaves of Cussonia racemosa, a Malagasy Endemic Plant. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50 (2), 268–71. DOI: 10.1248/cpb.50.268. Ding, Lan; Zhang, Zhang-Jing; Liu, Guo-An; Yang, Dong-Juan; Guo, Guo-Cong; Wang, Han; Sun, Kun Three New Cytotoxic ent-Kaurane Diterpenoids from Isodon weisiensis C. Y. Wu. Helv. Chim. Acta 2005, 88 (9), 2502–7. DOI: 10.1002/hlca.200590185. Batista, Ronan; García, Pablo A.; Castro, Maria A.; del Corral, José M. Miguel; San Feliciano, Arturo; de Oliveira, Alaíde B. New oxidized ent-kaurane and ent-norkaurane derivatives from kaurenoic acid. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2007, 18 (3), 622–27. DOI: 10.1590/S0103-50532007000300020. Zhao, Yong; Pu, Jian-Xin; Huang, Sheng-Xiong; Ding, Li-Sheng; Wu, Ying-Li; Li, Xian; Yang, Li-Bin; Xiao, Wei-Lie, et al. ent-Kaurane diterpenoids from Isodon pharicus. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72 (6), 988–93. PMID 19425589. DOI: 10.1021/np9000366.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 EC 4.2.3.19 – ent-kaurene synthase. In IUBMB Enzyme Nomenclature, <http://www.chem.qmul.ac.uk/iubmb/enzyme/EC4/2/3/19.html>. (accessed 18 September 2009). EC 1.14.13.78 – ent-kaurene oxidase. In IUBMB Enzyme Nomenclature, <http://www.chem.qmul.ac.uk/iubmb/enzyme/EC1/14/13/78.html>. (accessed 5 September 2009). EC 1.14.13.79 – ent-kaurenoic acid oxidase. In IUBMB Enzyme Nomenclature, <http://www.chem.qmul.ac.uk/iubmb/enzyme/EC1/14/13/79.html>. (accessed 5 September 2009).
- ↑ Nagashima, Fumihiro; Kondoh, Masuo; Uematsu, Toshinari; Nishiyama, Akiko; Saito, Sayaka; Sato, Masao; Asakawa, Yoshinori Cytotoxic and apoptosis-inducing ent-kaurane-type diterpenoids from the Japanese liverwort Jungermannia truncata nees. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50 (6), 808–13. DOI: 10.1248/cpb.50.808. Bruno, Maurizio; Piozzi, Franco; Arnold, Nelly Apostolides; Başer, K. Hüsnü Can; Tabanca, Nurhayat; Kirimer, Neşe Kaurane Diterpenoids from Three Sideritis Species. Turk. J. Chem. 2005, 29 (1), 61–64, <http://journals.tubitak.gov.tr/chem/issues/kim-05-29-1/kim-29-1-7-0402-1.pdf>. Kim, Ki Hyun; Choi, Sang Un; Lee, Kang Ro Diterpene glycosides from the seeds of Pharbitis nil. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72 (6), 1121–27. PMID 19435339. DOI: 10.1021/np900101t.
- ↑ Jaitak, Vikas; Bikram Singh, Bandna; Kaul, V. K. An efficient microwave-assisted extraction process of stevioside and rebaudioside-A from Stevia rebaudiana (Bertoni). Phytochem. Anal. 2009, 20 (3), 240–45. PMID 19358287. DOI: 10.1002/pca.1120.
- ↑ Brandle, J. E.; Telmer, P. G. Steviol glycoside biosynthesis. Phytochemistry 2007, 68 (14), 1855–63. DOI: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.02.010.
- ↑ Pelletier, S. William; Mody, Naresh V. The Chemistry of C20-Diterpenoid Alkaloids. In The Alkaloids: Chemistry and Pharmacology; Manske, R. H. F.; Rodrigo, R. G. A., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, 1981; Vol. 18, pp 102–21. ISBN 0-12-469518-3.
Further reading
- Lee, Jeong-Hyung; Koo, Tae Hyeon; Hwang, Bang Yeon; Lee, Jung Joon Kaurane Diterpene, Kamebakaurin, Inhibits NF-κB by Directly Targeting the DNA-binding Activity of p50 and Blocks the Expression of Antiapoptotic NF-κB Target Genes. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277 (21), 18411–20. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M201368200.
- Masamune, Satoru Total Syntheses of Diterpenes and Diterpene Alkaloids. II. A Tetracyclic Common Intermediate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86 (2), 288–89. DOI: 10.1021/ja01056a040.
- Maimone, Thomas J.; Baran, Phil S. Modern synthetic efforts toward biologically active terpenes. Nature Chem. Biol. 2007, 3, 396–407. DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.2007.1.
External links
- Kaurane Chemical Structure (shows the IUPAC conventional structure)
- Diterpenes, Kaurane – Research News and Information
| Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination |
This page is currently licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license and any later versions of that license. |