Difference between revisions of "Caesium chromate"
Physchim62 (talk | contribs) (Imported from http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Caesium_chromate&oldid=309892640) |
Physchim62 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| ImageFile = | | ImageFile = | ||
| ImageSize = | | ImageSize = | ||
| − | | IUPACName = | + | | IUPACName = caesium chromate |
| OtherNames = | | OtherNames = | ||
| Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | | Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| + | | InChI = 1/Cr.2Cs.4O/q;2*+1;;;2*-1/rCrO4.2Cs/c2-1(3,4)5;;/q-2;2*+1 | ||
| + | | StdInChI = 1S/Cr.2Cs.4O/q;2*+1;;;2*-1 | ||
| + | | InChIKey = BROHICCPQMHYFY-UICSPCLAAP | ||
| + | | StdInChIKey = BROHICCPQMHYFY-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| CASNo = 13454-78-9 | | CASNo = 13454-78-9 | ||
| EINECS = 236-640-4 | | EINECS = 236-640-4 | ||
| ChemSpiderID = 55521 | | ChemSpiderID = 55521 | ||
| PubChem = 61613 | | PubChem = 61613 | ||
| − | |||
| RTECS = | | RTECS = | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Line 26: | Line 29: | ||
}} | }} | ||
| Section7 = {{Chembox Hazards | | Section7 = {{Chembox Hazards | ||
| − | | | + | | Reference = <ref>{{CLP Regulation|index=024-017-00-8|page=419}}</ref>{{CFR chromium}}.</ref> |
| − | | EUIndex = 024-017-00-8 | + | | EUIndex = 024-017-00-8 <!-- hazards as chromium(VI) compound --> |
| − | | | + | | GHSPictograms = {{GHS08|Carc. 1B}}{{GHS07|Skin Sens. 1}}{{GHS09|Aquatic Acute 1, Aquatic Chronic 1}} |
| − | | | + | | GHSSignalWord = DANGER |
| + | | HPhrases = {{H-phrases|350|317|410}} | ||
| FlashPt = non-flammable | | FlashPt = non-flammable | ||
| − | | PEL = | + | | PEL = 0.005 mg/m<sup>3</sup> (as CrO<sub>3</sub>) |
}} | }} | ||
| Section8 = {{Chembox Related | | Section8 = {{Chembox Related | ||
| Line 41: | Line 45: | ||
}} | }} | ||
}} | }} | ||
| − | '''Caesium chromate''' is used to produce [[caesium]] vapour by reaction with silicon or boron, which is used to in the final stages of creating [[vacuum tubes]]; the caesium vapour reacts with the remaining gases, including [[nitrogen]] and [[oxygen]].<ref>{{citation | title = Nature's Building Blocks: An A-Z Guide to the Elements | first = John | last = Emsley | year = 2001 | publisher = Oxford University Press | | + | |
| + | '''Caesium chromate''' is used to produce [[caesium]] vapour by reaction with silicon or boron, which is used to in the final stages of creating [[vacuum tubes]]; the caesium vapour reacts with the remaining gases, including [[nitrogen]] and [[oxygen]].<ref>{{citation | title = Nature's Building Blocks: An A-Z Guide to the Elements | first = John | last = Emsley | year = 2001 | publisher = Oxford University Press | location = Oxford | isbn = 0198503407 | page = 81}}.</ref> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Further reading== | ||
| + | *{{IARC chromium}}. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==External links== | ||
| + | *{{PGCH|0138}} | ||
[[Category:Caesium compounds]] | [[Category:Caesium compounds]] | ||
[[Category:Chromates]] | [[Category:Chromates]] | ||
| + | [[Category:GHS category 1B carcinogens]] | ||
{{Imported from Wikipedia|name=Caesium chromate|id=309892640}} | {{Imported from Wikipedia|name=Caesium chromate|id=309892640}} | ||
Revision as of 08:09, 25 August 2009
| Caesium chromate | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | caesium chromate |
| Identifiers | |
| InChI | InChI=1/Cr.2Cs.4O/q;2*+1;;;2*-1/rCrO4.2Cs/c2-1(3,4)5;;/q-2;2*+1 |
| InChIKey | BROHICCPQMHYFY-UICSPCLAAP |
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/Cr.2Cs.4O/q;2*+1;;;2*-1 |
| Standard InChIKey | BROHICCPQMHYFY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| CAS number | [] |
| EC number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| PubChem | |
| Properties[1] | |
| Molecular formula | CrCs2O4 |
| Molar mass | 381.8 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow crystalline solid |
| Density | 4.237 g/cm3 |
| Solubility in water | 71.4 g/100 ml (13 ºC) |
| Hazards[2]Template:CFR chromium.</ref> | |
| EU index number | 024-017-00-8 |
| GHS pictograms | 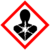 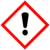 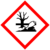
|
| GHS signal word | DANGER |
| GHS hazard statements | H350, H317, H410 |
| Flash point | non-flammable |
| PEL (U.S.) | 0.005 mg/m3 (as CrO3) |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Caesium sulfate |
| Other cations | Sodium chromate Potassium chromate Ammonium chromate |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
Caesium chromate is used to produce caesium vapour by reaction with silicon or boron, which is used to in the final stages of creating vacuum tubes; the caesium vapour reacts with the remaining gases, including nitrogen and oxygen.[3]
References
- ↑ CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 62nd ed.; Weast, Robert C., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, 1981; p B-91. ISBN 0-8493-0462-8.
- ↑ Index no. 024-017-00-8 of Annex VI, Part 3, to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures, amending and repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC, and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006. OJEU L353, 31.12.2008, pp 1–1355 at p 419.
- ↑ Emsley, John Nature's Building Blocks: An A-Z Guide to the Elements; Oxford University Press: Oxford, 2001; p 81. ISBN 0198503407.
Further reading
- Chromium and Chromium Compounds. In Chromium, Nickel and Welding; IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans 49; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 1990; pp 49–446. ISBN 92-832-1249-5.
External links
| Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination | |
This page was originally imported from Wikipedia, specifically this version of the article "Caesium chromate". Please see the history page on Wikipedia for the original authors. This WikiChem article may have been modified since it was imported. It is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution–Share Alike 3.0 Unported license. |