Difference between revisions of "Calcium hydride"
Physchim62 (talk | contribs) (Created page with ''''Calcium hydride''', CaH<sub>2</sub>, is an ionic (or "saline") hydride. It is used as a drying agent, particularly for organic solvents ==Refer…') |
Physchim62 (talk | contribs) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{chembox | ||
| + | | Name = Calcium hydride | ||
| + | | IUPACName = Calcium hydride | ||
| + | | Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| + | | ChemSpiderID = 94784 | ||
| + | | InChI = 1/Ca.2H/q+2;2*-1 | ||
| + | | InChIKey = UUGAXJGDKREHIO-UHFFFAOYAG | ||
| + | | StdInChI=1S/Ca.2H/q+2;2*-1 | ||
| + | | StdInChIKey = FAQLAUHZSGTTLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| + | | CASNo = 7789-78-8 | ||
| + | | CASNo_Ref = {{cascite}} | ||
| + | | EINECS = 232-189-2 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section2 = {{Chembox Properties | ||
| + | | Reference = <ref>{{RubberBible62nd|page=B-87}}.</ref> | ||
| + | | Formula = CaH<sub>2</sub> | ||
| + | | MolarMass = 42.094 g mol<sup>–1</sup> | ||
| + | | Appearance = grey powder (white when pure) | ||
| + | | Density = 1.9 g cm<sup>–3</sup> | ||
| + | | Solubility = reacts | ||
| + | | MeltingPt = 816 °C (under H<sub>2</sub>) | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section3 = {{Chembox Structure | ||
| + | | Reference = <ref>{{Greenwood&Earnshaw1st|page=72}}.</ref><ref>{{Wells5th}}.</ref> | ||
| + | | CrystalStruct = [[Lead chloride structure|PbCl<sub>2</sub>]], [[Pearson symbol|oP12]] | ||
| + | | SpaceGroup = P''nma'' (No. 62) | ||
| + | | Coordination = Tricapped trigonal prismatic (Ca<sup>2+</sup>) | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section7 = {{Chembox Hazards | ||
| + | | Reference = <ref>{{CLP Regulation|index=001-002-00-4|page=340}}</ref> | ||
| + | | EUIndex = 001-004-00-5 | ||
| + | | GHSPictograms = {{GHS02|Water-react. 1}} | ||
| + | | GHSSignalWord = DANGER | ||
| + | | HPhrases = {{H-phrases|260}} | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section8 = {{Chembox Related | ||
| + | | OtherCations = [[Beryllium hydride]]<br/>[[Magnesium hydride]]<br/>[[Strontium hydride]]<br/>[[Barium hydride]] | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | }} | ||
'''Calcium hydride''', CaH<sub>2</sub>, is an [[Ionic compound|ionic]] (or "saline") [[hydride]]. It is used as a [[drying agent]], particularly for [[organic solvent]]s | '''Calcium hydride''', CaH<sub>2</sub>, is an [[Ionic compound|ionic]] (or "saline") [[hydride]]. It is used as a [[drying agent]], particularly for [[organic solvent]]s | ||
| Line 6: | Line 45: | ||
==External links== | ==External links== | ||
{{wikipedia|Calcium hydride}} | {{wikipedia|Calcium hydride}} | ||
| − | * | + | *{{OrgSynth preps|id=39312|name=calcium hydride}} |
[[Category:Calcium compounds]] | [[Category:Calcium compounds]] | ||
| − | [[Category: | + | [[Category:Metal hydrides]] |
[[Category:Drying agents]] | [[Category:Drying agents]] | ||
{{CC-BY-3.0}} | {{CC-BY-3.0}} | ||
Latest revision as of 12:39, 20 June 2010
| Calcium hydride | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | Calcium hydride |
| Identifiers | |
| InChI | InChI=1/Ca.2H/q+2;2*-1 |
| InChIKey | UUGAXJGDKREHIO-UHFFFAOYAG |
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/Ca.2H/q+2;2*-1 |
| Standard InChIKey | FAQLAUHZSGTTLN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| CAS number | [] |
| EC number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Properties[1] | |
| Chemical formula | CaH2 |
| Molar mass | 42.094 g mol–1 |
| Appearance | grey powder (white when pure) |
| Density | 1.9 g cm–3 |
| Melting point |
816 °C (under H2) |
| Solubility in water | reacts |
| Structure[2][3] | |
| Crystal structure | PbCl2, oP12 |
| Space group | Pnma (No. 62) |
| Coordination geometry | Tricapped trigonal prismatic (Ca2+) |
| Hazards[4] | |
| EU index number | 001-004-00-5 |
| GHS pictograms | 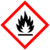
|
| GHS signal word | DANGER |
| GHS hazard statements | H260 |
| Related compounds | |
| Other cations | Beryllium hydride Magnesium hydride Strontium hydride Barium hydride |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
Calcium hydride, CaH2, is an ionic (or "saline") hydride. It is used as a drying agent, particularly for organic solvents
References
- ↑ CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 62nd ed.; Weast, Robert C., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, 1981; p B-87. ISBN 0-8493-0462-8.
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, A. Chemistry of the Elements; Pergamon: Oxford, 1984; p 72. ISBN 0-08-022057-6.
- ↑ Wells, A. F. Structural Inorganic Chemistry, 5th ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, 1984. ISBN 0-19-855370-6.
- ↑ Index no. 001-002-00-4 of Annex VI, Part 3, to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures, amending and repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC, and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006. OJEU L353, 31.12.2008, pp 1–1355 at p 340.
External links
| See also the corresponding article on Wikipedia. |
| Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination |
This page is currently licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license and any later versions of that license. |