Difference between revisions of "Hexyllithium"
Physchim62 (talk | contribs) (Created page with ''''''n''-Hexyllithium''', C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>13</sub>Li, sometimes abbreviated to '''HxLi''' or '''NHL''', is an organolithium compound used in organic synthesis as a [[s…') |
Physchim62 (talk | contribs) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{chembox | ||
| + | | Name = ''n''-Hexyllithium | ||
| + | | IUPACName = Hexyllithium | ||
| + | | OtherNames = HxLi, NHL | ||
| + | | Section1 = {{Chembox Identifiers | ||
| + | | InChI=1/C6H13.Li/c1-3-5-6-4-2;/h1,3-6H2,2H3;/rC6H13Li/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7/h2-6H2,1H3 | ||
| + | | StdInChI = 1S/C6H13.Li/c1-3-5-6-4-2;/h1,3-6H2,2H3; | ||
| + | | InChIKey = RMKNFFPDYCVCDI-ZLJYRZARAB | ||
| + | | StdInChIKey = RMKNFFPDYCVCDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| + | | EC-number = 404-950-0 | ||
| + | | CASNo = 21369-64-2 | ||
| + | | ChemSpiderID = 10626845 | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section2 = {{Chembox Properties | ||
| + | | Reference = | ||
| + | | Formula = C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>13</sub>Li | ||
| + | | MolarMass = 92.11 g mol<sup>−1</sup> | ||
| + | | Appearance = | ||
| + | | Density = | ||
| + | | Solubility = reacts violently | ||
| + | | MeltingPt = | ||
| + | | BoilingPt = | ||
| + | | pKa = approx. 40 <!-- unreferenced --> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section7 = {{Chembox Hazards | ||
| + | | Reference = <ref>{{CLP Regulation|index=003-002-00-X|page=340}}</ref> | ||
| + | | EUIndex = 003-002-00-X | ||
| + | | GHSPictograms = {{GHS02|Water-react. 1, Pyr. Sol. 1}}{{GHS05|Skin Corr. 1A}} | ||
| + | | GHSSignalWord = DANGER | ||
| + | | HPhrases = {{H-phrases|260|250|314}} <ref group="note">Within the European Union, the following additional hazard statement (EUH014) must also be displayed on labelling: Reacts violently with water.</ref> | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | | Section8 = {{Chembox Related | ||
| + | | OtherFunctn = [[Methyllithium]]<br/>[[Butyllithium|''n''-Butyllithium]]<br/>[[Tert-Butyllithium|''tert''-Butyllithium]] | ||
| + | | Function = [[organolithium compound]]s | ||
| + | }} | ||
| + | }} | ||
'''''n''-Hexyllithium''', C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>13</sub>Li, sometimes abbreviated to '''HxLi''' or '''NHL''', is an [[organolithium compound]] used in [[organic synthesis]] as a [[strong base]] or as a [[lithiation]] reagent. | '''''n''-Hexyllithium''', C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>13</sub>Li, sometimes abbreviated to '''HxLi''' or '''NHL''', is an [[organolithium compound]] used in [[organic synthesis]] as a [[strong base]] or as a [[lithiation]] reagent. | ||
| − | ''n''-Hexyllithium has similar chemical properties to [[Butyllithium|''n''-butyllithium]] (BuLi). Its main advantage over BuLi, particularly in industrial use, is the production of liquid [[Hexane|''n''-hexane]] as a byproduct rather than gaseous (and highly flammable) [[butane]].<ref>{{citation | series = Comprehensive Organometallic Chemistry II | volume = 11 | title = Main-Group Metal Organometallics in Organic Synthesis | editor1-first = Edward W. | editor1-last = Abel | editor2 | + | ''n''-Hexyllithium has similar chemical properties to [[Butyllithium|''n''-butyllithium]] (BuLi). Its main advantage over BuLi, particularly in industrial use, is the production of liquid [[Hexane|''n''-hexane]] as a byproduct rather than gaseous (and highly flammable) [[butane]].<ref>{{citation | series = Comprehensive Organometallic Chemistry II | volume = 11 | title = Main-Group Metal Organometallics in Organic Synthesis | editor1-first = Edward W. | editor1-last = Abel | editor2-first = F. Gordon A. | editor2-last = Stone | editor3-first = Geoffrey | editor3-last = Wilkinson | publisher = Elsevier | year = 1995 | isbn = 0080423183 | page = 3}}.</ref> It is commercially available as a solution in [[mixed hexanes]], usually at a concentration of about 2 M for laboratory use or 33% for industrial use. |
| − | ==References== | + | ==Notes and references== |
| + | ===Notes=== | ||
| + | {{reflist|group=note}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
{{reflist}} | {{reflist}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==External links== | ||
| + | {{wikipedia|Hexyllithium}} | ||
[[Category:Organolithium compounds]] | [[Category:Organolithium compounds]] | ||
[[Category:Reagents for organic chemistry]] | [[Category:Reagents for organic chemistry]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{CC-BY-3.0}} | ||
Latest revision as of 15:09, 20 June 2010
| n-Hexyllithium | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | Hexyllithium |
| Other names | HxLi, NHL |
| Identifiers | |
| InChI | InChI=1/C6H13.Li/c1-3-5-6-4-2;/h1,3-6H2,2H3;/rC6H13Li/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7/h2-6H2,1H3 |
| InChIKey | RMKNFFPDYCVCDI-ZLJYRZARAB |
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C6H13.Li/c1-3-5-6-4-2;/h1,3-6H2,2H3; |
| Standard InChIKey | RMKNFFPDYCVCDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| CAS number | [] |
| EC number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Properties | |
| Chemical formula | C6H13Li |
| Molar mass | 92.11 g mol−1 |
| Solubility in water | reacts violently |
| Acidity (pKa) | approx. 40 |
| Hazards[1] | |
| EU index number | 003-002-00-X |
| GHS pictograms | 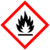 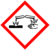
|
| GHS signal word | DANGER |
| GHS hazard statements | H260, H250, H314 [note 1] |
| Related compounds | |
| Other organolithium compounds | Methyllithium n-Butyllithium tert-Butyllithium |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
n-Hexyllithium, C6H13Li, sometimes abbreviated to HxLi or NHL, is an organolithium compound used in organic synthesis as a strong base or as a lithiation reagent.
n-Hexyllithium has similar chemical properties to n-butyllithium (BuLi). Its main advantage over BuLi, particularly in industrial use, is the production of liquid n-hexane as a byproduct rather than gaseous (and highly flammable) butane.[2] It is commercially available as a solution in mixed hexanes, usually at a concentration of about 2 M for laboratory use or 33% for industrial use.
Notes and references
Notes
- ↑ Within the European Union, the following additional hazard statement (EUH014) must also be displayed on labelling: Reacts violently with water.
References
- ↑ Index no. 003-002-00-X of Annex VI, Part 3, to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures, amending and repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC, and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006. OJEU L353, 31.12.2008, pp 1–1355 at p 340.
- ↑ Main-Group Metal Organometallics in Organic Synthesis; Abel, Edward W.; Stone, F. Gordon A.; Wilkinson, Geoffrey, Eds.; Comprehensive Organometallic Chemistry II; Elsevier, 1995; Vol. 11, p 3. ISBN 0080423183.
External links
| See also the corresponding article on Wikipedia. |
| Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination |
This page is currently licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license and any later versions of that license. |