Difference between revisions of "Sulfur dichloride"
Physchim62 (talk | contribs) (→Reactions) |
Physchim62 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
==Reactions== | ==Reactions== | ||
Sulfur dichloride is used as a precursor to [[organosulfur compound]]s, as it adds easily to C=C double bonds:<ref name="Bishop"/> a well-known example is in the manufacture of [[mustard gas]] from SCl<sub>2</sub> and [[ethylene]].<ref name="G&E"/> | Sulfur dichloride is used as a precursor to [[organosulfur compound]]s, as it adds easily to C=C double bonds:<ref name="Bishop"/> a well-known example is in the manufacture of [[mustard gas]] from SCl<sub>2</sub> and [[ethylene]].<ref name="G&E"/> | ||
| − | :SCl<sub>2</sub> + | + | :SCl<sub>2</sub> + 2 H<sub>2</sub>C=CH<sub>2</sub> → ClCH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>SCH<sub>2</sub>CH<sub>2</sub>Cl |
| − | Fluorination of SCl<sub>2</sub> with [[sodium fluoride]] leads to [[disproportionation]], and provides a convenient synthesis of [[sulfur tetrafluoride]], a versatile [[fluorinating | + | Fluorination of SCl<sub>2</sub> with [[sodium fluoride]] leads to [[disproportionation]], and provides a convenient synthesis of [[sulfur tetrafluoride]], a versatile [[fluorinating agent]].<ref>{{citation | first1 = C. W. | last1 = Tullock | first2 = F. S. | last2 = Fawcett | first3 = W. C. | last3 = Smith | first4 = D. D. | last4 = Coffman | title = The Chemistry of Sulfur Tetrafluoride. I. The Synthesis of Sulfur Tetrafluoride | journal = J. Am. Chem. Soc. | volume = 82 | issue = 3 | pages = 539–42 | year = 1960 | doi = 10.1021/ja01488a011}}.</ref><ref>{{citation | inventor1-last = Tullock | inventor1-first = Charles W. | assignee = Du Pont | title = Synthesis of sulfur tetrafluoride | country-code = US | patent-number = 2992073 | issue-date = 1961-07-11}}.</ref><ref>{{citation | journal = Inorg. Synth. | volume = 7 | pages = 119 | year = 1963}}.</ref> |
| − | : | + | :3 SCl<sub>2</sub> + 4 NaF → SF<sub>4</sub> + S<sub>2</sub>Cl<sub>2</sub> + 4 NaCl |
==Notes and references== | ==Notes and references== | ||
Revision as of 18:25, 17 September 2010
| Sulfur dichloride | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | sulfur dichloride |
| Other names | dichlorosulfane |
| Identifiers | |
| InChI | InChI=1/Cl2S/c1-3-2 |
| InChIKey | FWMUJAIKEJWSSY-UHFFFAOYAS |
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/Cl2S/c1-3-2 |
| Standard InChIKey | FWMUJAIKEJWSSY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| CAS number | [] |
| EC number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Properties[1] | |
| Chemical formula | SCl2 |
| Molar mass | 102.97 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | red liquid |
| Density | 1.621 g cm−3 |
| Melting point |
−122 °C |
| Boiling point |
59 °C decomp. |
| Solubility in water | reacts violently |
| Structure[1] | |
| Molecular geometry | bent |
| Thermochemistry[2] | |
| Std enthalpy of formation ΔfH |
−49.79 kJ mol−1 |
| Standard molar entropy S |
183.68 J K−1 mol−1 |
| Hazards[3] | |
| Material safety data sheet (MSDS) | ICSC |
| EU index number | 016-013-00-X |
| GHS pictograms | 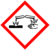 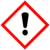 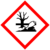
|
| GHS signal word | DANGER |
| GHS hazard statements | H314, H335, H400 |
| Related compounds | |
| Other chlorides of sulfur | Disulfur dichloride Sulfur tetrachloride Thionyl chloride Sulfuryl chloride |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
Sulfur dichloride, SCl2, is the highest thermally stable chloride of sulfur. It is also the first in a homologous series of dichlorosulfanes, SnCl2.
Contents
Preparation and purification
Sulfur dichloride is prepared by the chlorination of elemental sulfur, with disulfur dichloride as an intermediate.
- S8 + 4 Cl2 → 4 S2Cl2
- S2Cl2 + Cl2 → 2 SCl2
Sulfur dichloride is often contaminated with S2Cl2, but can be stabilized with a small amount of phosphorus pentachloride.[1] It is purified by distillation, often as an azeotrope with phosphorus trichloride (99% SCl2).[4]
Reactions
Sulfur dichloride is used as a precursor to organosulfur compounds, as it adds easily to C=C double bonds:[4] a well-known example is in the manufacture of mustard gas from SCl2 and ethylene.[1]
- SCl2 + 2 H2C=CH2 → ClCH2CH2SCH2CH2Cl
Fluorination of SCl2 with sodium fluoride leads to disproportionation, and provides a convenient synthesis of sulfur tetrafluoride, a versatile fluorinating agent.[5][6][7]
- 3 SCl2 + 4 NaF → SF4 + S2Cl2 + 4 NaCl
Notes and references
Notes
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, A. Chemistry of the Elements; Pergamon: Oxford, 1984; pp 815–16. ISBN 0-08-022057-6.
- ↑ Sulfur dichloride. In NIST Chemistry WebBook; National Institute for Standards and Technology, <http://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/inchi/InChI%3DInChI=1S/Cl2S/c1-3-2>. (accessed 17 September 2010).
- ↑ Index no. 013-003-00-7 of Annex VI, Part 3, to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures, amending and repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC, and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006. OJEU L353, 31.12.2008, pp 1–1355 at p 366.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Bishop, Roger 9-Thiabicyclo[3.3.1]nonane-2,6-dione. Org. Synth. 1992, 70, 120, <http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/orgsyn/prepContent.asp?prep=cv9p0692>; Coll. Vol., 9, 692.
- ↑ Tullock, C. W.; Fawcett, F. S.; Smith, W. C.; Coffman, D. D. The Chemistry of Sulfur Tetrafluoride. I. The Synthesis of Sulfur Tetrafluoride. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1960, 82 (3), 539–42. DOI: 10.1021/ja01488a011.
- ↑ Tullock, Charles W. (Du Pont) Synthesis of sulfur tetrafluoride. US Patent 2992073, issued 11 July 1961.
- ↑ Inorg. Synth. 1963, 7, 119.
External links
| See also the corresponding article on Wikipedia. |
| Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination |
This page is currently licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license and any later versions of that license. |