Difference between revisions of "3-Methylbut-3-en-1-ol"
Physchim62 (talk | contribs) |
Physchim62 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
| HPhrases = {{H-phrases|226|319}} | | HPhrases = {{H-phrases|226|319}} | ||
| PPhrases = {{P-phrases|210|233|240|241|242|243|264|280|303+361+353|305+351+338|337+313|370+378| 403+235|501}} | | PPhrases = {{P-phrases|210|233|240|241|242|243|264|280|303+361+353|305+351+338|337+313|370+378| 403+235|501}} | ||
| − | | FlashPt = 36 ºC (97 ºF) < | + | | FlashPt = 36 ºC (97 ºF)<ref group="note">Sigma-Aldrich Co. gives a value for the flash point of 3-methylbut-3-en-1-ol of 42 ºC (108 ºF). The difference in the two values does not alter the safety classification of 3-methylbut-3-en-1-ol as a category 3 flammable liquid under the [[Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals|GHS]]; but would make it a class IC flammable liquid ([[NFPA 704|NFPA class F3]]) instead of a class II combustible liquid ([[NFPA 704|NFPA class F2]]) under the U.S. [[Occupational Safety and Health Administration|OSHA]] classification (29 C.F.R § 1910.106).</ref> |
}} | }} | ||
| Section8 = {{Chembox Related | | Section8 = {{Chembox Related | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
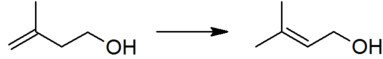
[[File:Prenol prepn.png|left|383px|The isomerization of isoprenol to prenol, the second step in the industrial manufacture of prenol.]]<br clear="left"/> | [[File:Prenol prepn.png|left|383px|The isomerization of isoprenol to prenol, the second step in the industrial manufacture of prenol.]]<br clear="left"/> | ||
The reaction is catalyzed by any species which can form an [[allyl complex]] without excessive [[hydrogenation]] of the substrate, for example poisoned palladium catalysts.<ref>See, eg, {{citation | first1 = S. B. | last1 = Kogan | first2 = M. | last2 = Kaliya | first3 = N. | last3 = Froumin | title = Liquid phase isomerization of isoprenol into prenol in hydrogen environment | journal = Appl. Catal. A: Gen. | volume = 297 | issue = 2 | year = 2006 | pages = 231–36 | doi = 10.1016/j.apcata.2005.09.010}}.</ref> | The reaction is catalyzed by any species which can form an [[allyl complex]] without excessive [[hydrogenation]] of the substrate, for example poisoned palladium catalysts.<ref>See, eg, {{citation | first1 = S. B. | last1 = Kogan | first2 = M. | last2 = Kaliya | first3 = N. | last3 = Froumin | title = Liquid phase isomerization of isoprenol into prenol in hydrogen environment | journal = Appl. Catal. A: Gen. | volume = 297 | issue = 2 | year = 2006 | pages = 231–36 | doi = 10.1016/j.apcata.2005.09.010}}.</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Notes== | ||
| + | {{reflist|group="note"}} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 20:09, 31 August 2009
| 3-Methylbut-3-en-1-ol | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | 3-Methylbut-3-en-1-ol |
| Other names | Isoprenol |
| Identifiers | |
| InChI | InChI=1/C5H10O/c1-5(2)3-4-6/h6H,1,3-4H2,2H3 |
| InChIKey | CPJRRXSHAYUTGL-UHFFFAOYAD |
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C5H10O/c1-5(2)3-4-6/h6H,1,3-4H2,2H3 |
| Standard InChIKey | CPJRRXSHAYUTGL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| CAS number | [] |
| EC number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Properties[1] | |
| Chemical formula | C5H10O |
| Molar mass | 86.132 g/mol |
| Density | 0.853 g/cm3 |
| Boiling point |
130–132 ºC |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.433 |
| Hazards[2] | |
| EU index number | not listed |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS signal word | WARNING |
| GHS hazard statements | H226, H319 |
| GHS precautionary statements | P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P264, P280, P303+361+353, P305+351+338, P337+313, P370+378, P403+235, P501 |
| Flash point | 36 ºC (97 ºF)[note 1] |
| Related compounds | |
| Other compounds | 3-Methylbut-2-en-1-ol |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
3-Methylbut-3-en-1-ol, also known as isoprenol, is a hemiterpene alcohol. It is produced industrially as an intermediate to 3-methylbut-2-en-1-ol (prenol): global production in 2001 can be estimated as 6–13 thousand tons.[3]
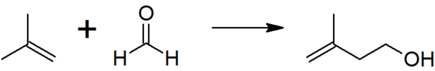
3-Methylbut-3-en-1-ol is produced by the reaction between 2-methylpropene (isobutene) and formaldehyde.
The thermodynamically preferred isomer with the more substituted double bond cannot be directly formed in this reaction, but isomerization yields the desired product:
The reaction is catalyzed by any species which can form an allyl complex without excessive hydrogenation of the substrate, for example poisoned palladium catalysts.[4]
Notes
- ↑ Sigma-Aldrich Co. gives a value for the flash point of 3-methylbut-3-en-1-ol of 42 ºC (108 ºF). The difference in the two values does not alter the safety classification of 3-methylbut-3-en-1-ol as a category 3 flammable liquid under the GHS; but would make it a class IC flammable liquid (NFPA class F3) instead of a class II combustible liquid (NFPA class F2) under the U.S. OSHA classification (29 C.F.R § 1910.106).
References
- ↑ Source: Sigma-Aldrich Co., product no. W519308 (data accessed 2009-08-31).
- ↑ HSNO Chemical Classification Information Database, <http://www.ermanz.govt.nz/Chemicals/ChemicalDisplay.aspx?SubstanceID=13375> (accessed 31 August 2009), New Zealand Environmental Risk Management Authority.
- ↑ 3-Methyl-2-buten-1-ol; SIDS Initial Assessment Report; Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, May 2005, <http://www.inchem.org/documents/sids/sids/556821.pdf>.
- ↑ See, eg, Kogan, S. B.; Kaliya, M.; Froumin, N. Liquid phase isomerization of isoprenol into prenol in hydrogen environment. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2006, 297 (2), 231–36. DOI: 10.1016/j.apcata.2005.09.010.
| Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination |
This page is currently licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license and any later versions of that license. |