Beryllium oxide
Revision as of 16:47, 20 June 2010 by Physchim62 (talk | contribs)
| Beryllium oxide | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Beryllia, Bromellite |
| Identifiers | |
| InChI | InChI=1/Be.O/rBeO/c1-2 |
| InChIKey | LTPBRCUWZOMYOC-SRAGPBHZAE |
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/Be.O |
| Standard InChIKey | LTPBRCUWZOMYOC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| CAS number | [] |
| EC number | |
| RTECS | DS4025000 |
| ChemSpider | |
| Properties[1] | |
| Chemical formula | BeO |
| Molar mass | 25.012 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 3.01 g cm−3 |
| Melting point |
2530(30) °C |
| Boiling point |
approx. 3900 °C |
| Solubility in water | 200 µg dm−3 |
| Band gap | 10.6 eV |
| Thermal conductivity | 40 mW m−1 K−1 |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.719, 1.733 |
| Structure[2] | |
| Crystal structure | Wurtzite, hP4 |
| Space group | P63/mc (No. 186) |
| Thermochemistry[3] | |
| Std enthalpy of formation ΔfH |
–609.4(25) kJ mol−1 |
| Standard molar entropy S |
13.77(4) J K–1 mol–1 |
| Hazards[4][5] | |
| Material safety data sheet (MSDS) | ICSC |
| EU index number | 004-003-00-8 |
| GHS pictograms | 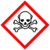 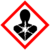
|
| GHS signal word | DANGER |
| GHS hazard statements | H350, H330, H301, H372, H319, H335, H315, H317 |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| PEL (U.S.) | 0.002 mg m−3 TWA (as Be) 0.005 mg m−3 30 min. (as Be) 0.025 mg m−3 peak (as Be) |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Beryllium sulfide Beryllium selenide Beryllium telluride |
| Other cations | Magnesium oxide Calcium oxide Strontium oxide Barium oxide |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
Beryllium oxide, BeO, is an amphoteric oxide.[2] As with all beryllium compounds, it is highly carcinogenic.[6]
References
- ↑ CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 62nd ed.; Weast, Robert C., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, 1981; p 82. ISBN 0-8493-0462-8.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, A. Chemistry of the Elements; Pergamon: Oxford, 1984; pp 131–33. ISBN 0-08-022057-6.
- ↑ Cox, J. D.; Wagman, D. D.; Medvedev, V. A. CODATA Key Values for Thermodynamics; Hemisphere: New York, 1989. ISBN 0891167587, <http://www.codata.org/resources/databases/key1.html>.
- ↑ Index no. 004-003-00-8 of Annex VI, Part 3, to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures, amending and repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC, and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006. OJEU L353, 31.12.2008, pp 1–1355 at p 341.
- ↑ Beryllium and beryllium compounds. In Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (NIOSH) Publication No. 2005-149; Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, 2005. ISBN 9780160727511, <http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0054.html>.
- ↑ Beryllium and Beryllium Compounds. In Beryllium, Cadmium, Mercury, and Exposures in the Glass Manufacturing Industry; IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans 58; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 1993; pp 41–117. ISBN 92-832-1258-4, <http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Monographs/vol58/mono58-6.pdf>.
External links
| See also the corresponding article on Wikipedia. |
- International Chemical Safety Card 1325
- IPCS Environmental Health Criteria 106: Beryllium
- IPCS Concise International Chemical Assessment Document 32: Beryllium and Beryllium Compounds
- IPCS Health and Safety Guide 044: Beryllium
- Entry for "Beryllium and compounds" on the Australian National Pollutant Inventory
- Beryllium and beryllium compounds, NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards
| Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination |
This page is currently licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license and any later versions of that license. |