Potassium biiodate
Revision as of 18:16, 9 September 2010 by Physchim62 (talk | contribs)
| Potassium biiodate | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name | potassium µ-hydridobis(trioxidoiodate)(1−) |
| Other names | potassium hydrogen iodate |
| Identifiers | |
| InChI | InChI=1/2HIO3.K/c2*2-1(3)4;/h2*(H,2,3,4);/q;;+1/p-1 |
| InChIKey | ACAYDTMSDROWHW-REWHXWOFAC |
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/2HIO3.K/c2*2-1(3)4;/h2*(H,2,3,4);/q;;+1/p-1 |
| Standard InChIKey | ACAYDTMSDROWHW-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
| CAS number | [] |
| EC number | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Properties[1] | |
| Chemical formula | KH(IO3)2 |
| Molar mass | 389.91 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | white crystals |
| Solubility in water | 1.33 g/100 ml (15 °C) |
| Hazards[2][3][Note 1] | |
| EU index number | not listed |
| GHS pictograms | 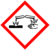 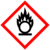 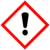
|
| GHS signal word | DANGER |
| GHS hazard statements | H272, H302, H314, H318 |
| GHS precautionary statements | P210, P220, P221, P260, P264, P270, P280, P301+312, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P363, P304+340, P310, P321 |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Related compounds | |
| Other compounds | Potassium iodate Iodic acid |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) | |
Potassium biiodate, KH(IO3)2, is a primary standard strong acid in analytical chemistry.
Notes and references
Notes
- ↑ Hazards were assessed as for an equimolar mixture of potassium iodate and iodic acid.
References
- ↑ CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 62nd ed.; Weast, Robert C., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, 1981; p B-133. ISBN 0-8493-0462-8.
- ↑ HSNO Chemical Classification Information Database, <http://www.ermanz.govt.nz/Chemicals/ChemicalDisplay.aspx?SubstanceID=1913> (accessed 9 September 2010), New Zealand Environmental Risk Management Authority.
- ↑ HSNO Chemical Classification Information Database, <http://www.ermanz.govt.nz/Chemicals/ChemicalDisplay.aspx?SubstanceID=12620> (accessed 9 September 2010), New Zealand Environmental Risk Management Authority.