Phosphorus tribromide
{{chembox | Name = Phosphorus tribromide | OtherNames = Tribromophosphane | Section1 = |- ! style="background: #F8EABA; text-align: center;" colspan="2" | Identifiers |-
|- | InChI || InChI=1/Br3P/c1-4(2)3 |- | InChIKey || IPNPIHIZVLFAFP-UHFFFAOYAL |- | Standard InChI || InChI=1S/Br3P/c1-4(2)3 |- | Standard InChIKey || IPNPIHIZVLFAFP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |- | CAS number || [] |- | EC number || |-
|- | UN number || 1808 |- | RTECS || TH4460000 |-
|- | ChemSpider || |-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|- | Section2 = |- ! style="background: #F8EABA; text-align: center;" colspan="2" | Properties[1][2][3] |- | Chemical formula || PBr3 |- | Molar mass || 270.69 g mol−1 |- | Appearance || colorless liquid |-
|- | Density || 2.852 g cm−3 |- | Melting point || −41.5 °C |- | Boiling point || 173.2 °C |-
|-
|- | Critical point || 438 °C (711 K) |- | Solubility in water || hydrolyzes |-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|- | Refractive index (nD) || 1.697 |-
|-
|-
|-
|-
| Section4 = |-
! style="background: #F8EABA; text-align: center;" colspan="2" | Thermochemistry[2]
|-
| Std enthalpy of formation ΔfHo298 || −146.02 kJ mol−1
|-
|-
|-
| Standard molar entropy So298 || 348.22 J K–1 mol–1
|-
|-
|-
|- | Section7 = |- ! style="background: #F8EABA; text-align: center;" colspan="2" | Hazards[4] |-
|-
|-
| EU index number || 015-103-00-6
|-
| GHS pictograms || style="text-align: center;" | 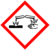
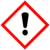 |-
| GHS signal word || DANGER
|-
| GHS hazard statements || H314, H335 [note 1]
|-
| GHS precautionary statements || P260, P261, P264, P271, P280, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P363, P304+340, P310, P312, P321, P305+351+338, P403+233
|-
|-
| GHS signal word || DANGER
|-
| GHS hazard statements || H314, H335 [note 1]
|-
| GHS precautionary statements || P260, P261, P264, P271, P280, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P363, P304+340, P310, P312, P321, P305+351+338, P403+233
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|-
|- Phosphorus tribromide, PBr3, is a colourless liquid which fumes in moist air. It is used as a reagent in organic synthesis, where it converts alcohols into bromoalkanes.[5]
Notes and references
Notes
- ↑ Within the European Union, the following additional hazard statement (EUH014) must also be displayed on labelling: Reacts violently with water.
References
- ↑ CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 62nd ed.; Weast, Robert C., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, 1981; p B-127. ISBN 0-8493-0462-8.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Phosphorus tribromide. In NIST Chemistry WebBook; National Institute for Standards and Technology, <http://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/inchi/InChI%3D1S/Br3P/c2-1(3)4>. (accessed 7 January 2011).
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, A. Chemistry of the Elements; Pergamon: Oxford, 1984; pp 568–70. ISBN 0-08-022057-6.
- ↑ Index no. 015-103-00-6 of Annex VI, Part 3, to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on classification, labelling and packaging of substances and mixtures, amending and repealing Directives 67/548/EEC and 1999/45/EC, and amending Regulation (EC) No 1907/2006. OJEU L353, 31.12.2008, pp 1–1355 at p 386.
- ↑ Ukeles, S. D.; Freiberg, M. Bromine, Inorganic Compounds. In Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; John Wiley: New York, 2002. DOI: 10.1002/0471238961.021815131001031.
External links
| See also the corresponding article on Wikipedia. |
| Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination |
This page is currently licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported license and any later versions of that license. |